Linux**
- MySQL-Database; SELinux Policy
SELinux
(Security-Enhanced-Linux) is a fine granulated protection introduced
with Linux Kernel 2.6.
SELinux
controls the access of processes not only to files - but also to
devices, sockets, ports and other processes.
If a process needs
access to an object controlled by SELinux, this has to be permitted
by a policy; i.e. permitting commands in a text-file.
Overview:
Disabling
SELinux
Setting
a SELinux-Policy for MySQL-Database (not
yet written)
Disabling
SELinux
Open
the application for setting firewalls and SELinux parameters:
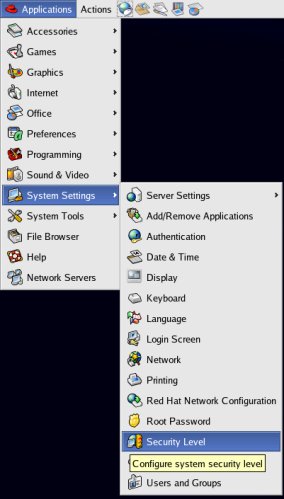
Select
>Applications>System
Settings>Security Level.
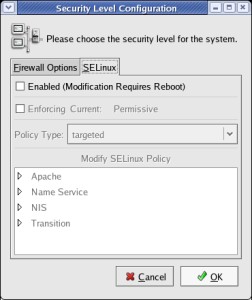
In
the 'Security Level Configuration' window click the 'SELinux'
tab.
Uncheck the
'Enabled (Modification Requieres Reboot) mark.
Click the
[ OK ] button thereafter.
Thereafter
a 'Warning' window appears, telling that the security level and the
firewall will be overridden.
Confirm this warning by click
the
[ Yes ] button.
The
change requieres a restart of the machine !
To
top of document
Test
top.
Setting
a SELinux-Policy for MySQL-Database
To
be written.
To
top of document